
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Decrease and Conquer
Reduce the problem in smaller units of the same problem.
And solve a smaller problem.
Find the original solution extending solution of smaller problem.
Example
{ 1 }
DFS (Depth - First - Search)
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures.
-
Usually start at A
-
In alphabetical order, choose next node.
-
Down until there is no more choice below.
-
If there is not node, back to another cross.
BFS (Breadth - First - Search)
{ 2 }
Breadth-first search (BFS) is an algorithm for searching tree or graph like DFS.
-
Usually start A.
-
In alphabetical order, choose next node
-
Unlike DFS, BFS visit same line node first.
-
If there is not node on same line, down to child node
GROUP PROJECT
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Numbers Game
This program is Numbers Game.
It is win when User find the answer which computer think.
-
Input the number.
-
If the answer is multiple of input,
the multiples do not erase.
Else, multiples erase. -
Repeat step2, then user think what is answer.
-
Decrease by one : reduce problem into one.
- Depth-first-search
- Breadth-first-search -
Decrease by a constant factor : reduce problem into constant unit.
- Fake Coin Puzzle
- Russian peasant
- Josephus problem -
Variable-size decrease. : reduce problem in variable-size unit
- Euclid's algorithm for greatest common divisor
- Selection problem
- Binary search Tree
What kind of decrease and conquer algorithm?
What is the difference?
Decrease and Conquer
After dividing the problem into smaller units, part which seems to be not answer has not been confirmed
Divide and Conquer
Solve each problem after the original problem is divided in two units
Brute Force
Check all of the case about problem
Binary Search Tree
{ 3 }
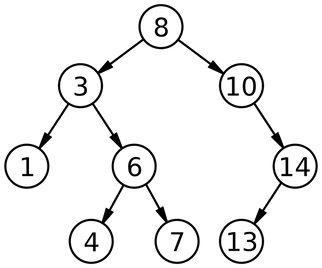
Key Point
-
The parent node is larger than left-child node.
-
The parent node is smaller than right-child.
-
Start at the highest node.
-
If element smaller than node, down to left.
Else, down to right. -
Repeat this step2 until finding the element.
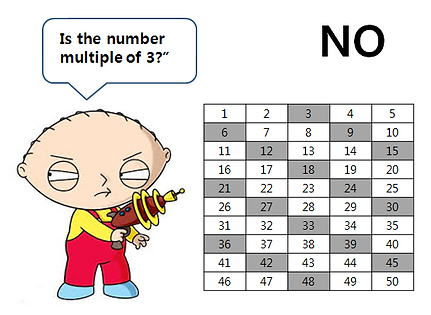
SOLUTION
